
In today’s visually driven world, the ability to communicate ideas through striking visuals is more crucial than ever. Whether you’re an aspiring artist, a marketing professional, or someone looking to pivot into a creative career, a graphic design course can be your gateway to mastering the art of visual storytelling.
As businesses increasingly rely on visual content to engage audiences and convey messages, the demand for skilled graphic designers continues to rise. This blog will explore the fundamentals of graphic design courses, the skills you can expect to learn, and how these courses can pave the way for a fulfilling and dynamic career in the creative industry.
What is Graphic Designing?
Graphic design is the craft of creating visual content to communicate messages. By applying visual hierarchy and page layout techniques, designers use typography and images to meet users’ specific needs and focus on the logic of displaying elements in interactive designs to optimize the user experience. Graphic design encompasses a wide range of activities, from developing logos and branding materials to designing websites and print media. At its core, graphic design is about solving problems through visual communication.
Key Elements of Graphic Design:
- Typography: The art of arranging text to make written language legible, readable, and visually appealing. Typography is crucial in setting the tone and ensuring readability.
- Color Theory: Understanding how colors interact, the emotional impact of different colors, and how to create harmonious color palettes. Colors can evoke emotions and influence perception.
- Layout and Composition: The arrangement of visual elements on a page. Good layout and composition ensure that the design is balanced and guides the viewer’s eye in a logical way.
- Imagery: The use of images, whether photographs, illustrations, or icons, to enhance communication. Imagery can make abstract concepts more tangible and memorable.
- Design Principles: Foundational rules that guide the organization of visual elements, including balance, contrast, emphasis, movement, proportion, and rhythm. These principles help create cohesive and effective designs.
Applications of Graphic Designing course:
- Brand Identity: Creating logos, business cards, letterheads, and other branding materials that define a company’s visual identity.
- Advertising: Designing posters, banners, and other promotional materials that capture attention and convey marketing messages.
- Web Design: Crafting visually appealing and user-friendly websites, focusing on layout, color schemes, and user experience.
- Print Design: Producing magazines, brochures, flyers, and other print materials that communicate information in a visually engaging way.
- Digital Media: Developing graphics for social media, email marketing, and other digital platforms to engage and inform audiences.
In essence, graphic design is a powerful tool for storytelling and communication. It blends creativity with technology, allowing designers to create visual solutions that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also functional and impactful.
What to Expect in a Graphic Design Course?
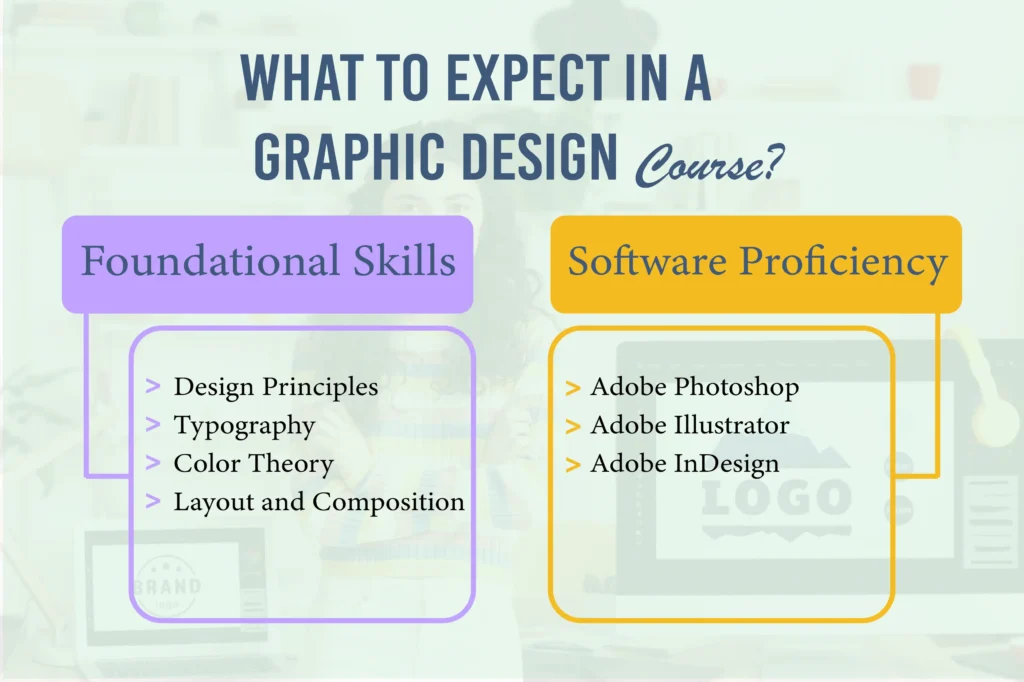
Embarking on a graphic design course is an exciting journey that combines creativity, technology, and communication. These courses are designed to equip you with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in the dynamic field of graphic design. Here’s what you can expect:
Foundational Skills
A good graphic design course starts with the basics, laying a solid foundation for more advanced concepts. You’ll learn about:
- Design Principles: These are the core concepts that guide the creation of visually appealing and effective designs. Principles like balance, contrast, harmony, and hierarchy help designers organize visual elements in a way that enhances the viewer’s experience.
- Typography: Typography is the art of arranging text. You’ll learn about different typefaces, how to choose the right fonts, and how to arrange text in a visually appealing and readable manner. Understanding typography is crucial as it greatly impacts the design’s overall look and feel.
- Color Theory: This involves understanding how colors interact, how they can be combined harmoniously, and the psychological effects they have on viewers. You’ll learn about color models, schemes, and the importance of color in design.
- Layout and Composition: These principles involve the arrangement of text, images, and other elements on a page. Good layout and composition ensure that the design is visually balanced and guides the viewer’s eye in a logical and effective manner.
Software Proficiency
Graphic design heavily relies on specialized software tools. Courses will typically cover:
- Adobe Photoshop: A powerful tool for image editing and manipulation. You’ll learn to enhance photos, create digital paintings, and produce complex compositions.
- Adobe Illustrator: Essential for creating vector graphics, which are crucial for logo design, illustrations, and any artwork that requires scaling without losing quality.
- Adobe InDesign: This tool is used for layout design, particularly for print media like magazines, brochures, and flyers. It helps you arrange text and images in a clean and professional manner.
Project-Based Learning
Hands-on projects are a cornerstone of graphic design courses. These projects simulate real-world scenarios and can include:
- Brand Identity Design: Creating a cohesive visual identity for a brand, including logos, business cards, and other branding materials.
- Web Design: Designing website layouts, user interfaces, and user experiences. This involves not just the visual aspect but also understanding how design affects functionality and user interaction.
- Print Design: Designing brochures, posters, magazines, and other print materials. You’ll learn about the specific considerations for print media, such as resolution, color modes, and bleed.
- Digital Media: Creating graphics for social media, banner ads, and email marketing templates. This also includes understanding the requirements and limitations of various digital platforms.
Feedback and Critique
Constructive feedback is crucial for growth. Instructors and peers will provide critiques, helping you refine your work and develop a critical eye for design. Learning to give and receive feedback is an important part of the design process, as it helps you improve your skills and learn from different perspectives.
Additional Components
- History and Theory of Graphic Design: Understanding the evolution of design and its cultural and historical contexts.
- Portfolio Development: Building a professional portfolio that showcases your best work. This is essential for job applications and attracting clients.
- Networking Opportunities: Connecting with industry professionals, attending design events, and participating in online communities.
Career Paths in Graphic Design

Completing a graphic design course opens up a myriad of exciting career opportunities across various industries. As the demand for visual content continues to grow, so does the need for talented graphic designers. Here are some of the most promising career paths in graphic design:
Graphic Designer
As a graphic designer, you’ll work on a variety of projects, creating visual concepts that inspire, inform, and captivate consumers. This role often involves:
- Designing logos, brochures, advertisements, and other marketing materials.
- Working with clients to understand their needs and create designs that meet their objectives.
- Collaborating with other creative professionals, such as writers, photographers, and web developers.
Brand Identity Designer
Brand identity designers specialize in creating the visual aspects of a brand’s identity. This includes:
- Developing logos, color schemes, typography, and other design elements that represent a brand.
- Ensuring consistency across all visual materials, from business cards to packaging.
- Creating brand guidelines to maintain a cohesive look across all platforms.
Web Designer
Web designers focus on creating visually appealing and user-friendly websites. Their responsibilities include:
- Designing the layout, color scheme, and graphics for websites.
- Ensuring that websites are responsive and work well on various devices.
- Collaborating with developers to implement designs and improve user experience.
User Experience (UX) Designer
UX designers concentrate on the overall feel of the product and ensure that users have a seamless experience. Their tasks involve:
- Conducting user research to understand the needs and behaviors of users.
- Creating wireframes, prototypes, and user flows.
- Testing designs and gathering feedback to make improvements.
Print Designer
Print designers create visual content for physical media. This role includes:
- Designing layouts for magazines, newspapers, brochures, and posters.
- Working with printers to ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications.
- Understanding the technical aspects of print production, such as color profiles and bleed areas.
Illustrator
Illustrators create original artwork for various media, including books, magazines, advertisements, and digital platforms. Their work involves:
- Developing unique illustrations that convey specific messages or concepts.
- Collaborating with authors, editors, and art directors to produce visually engaging content.
- Utilizing both traditional drawing skills and digital tools.
Art Director
Art directors oversee the visual aspects of projects and guide creative teams. Their responsibilities include:
- Setting the visual style and direction for campaigns, magazines, product packaging, and more.
- Leading a team of designers, photographers, and other creatives.
- Ensuring that the visual elements align with the client’s vision and goals.
Motion Graphic Designer
Motion graphic designers create animated graphics for various media, including film, television, and digital platforms. Their tasks involve:
- Designing and animating graphics that move, such as title sequences, explainer videos, and advertisements.
- Using software like After Effects and Cinema 4D to bring designs to life.
- Collaborating with video editors and producers to integrate motion graphics into larger projects.
Freelance Designer
Freelance designers work independently, offering their design services to various clients. This role provides:
- Flexibility to choose projects and clients.
- Opportunity to work on a diverse range of projects.
- The need to manage all aspects of the business, from marketing and client acquisition to project management and billing.
Conclusion
Starting a graphic design course is more than just going to school; it’s a way to enter a world where creativity and technology come together to create powerful visuals. Whether you want to be a skilled graphic designer, a branding expert, a web designer, or explore other career options in this exciting field, the basic skills and hands-on experience you gain from a graphic design course will help you succeed in the creative industry.
As businesses use more visual content to engage and captivate their audiences, the demand for talented graphic designers is increasing. Being able to create visuals that effectively communicate messages is a highly valued skill in various areas, from advertising and marketing to web development and digital media.
Additionally, creating a professional portfolio during your course will showcase your best work and help you in job searches or freelance work. Networking opportunities and industry insights from your course will further boost your career prospects, opening doors to exciting opportunities and collaborations.
You can join our course by clicking the following link
